
The Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL) plays several critical roles in a typical fuel cell application and is often integrated as part of the Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA). Typical applications that use GDLs consist of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC) and Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFC). When a GDL is coated with a catalyst it is then referred to as a Gas Diffusion Electrode(GDE), which is sometimes sold or installed separately from the Membrane or MEA. Acting as an electrode is the easy part of the GDL/GDE, though.
What Does a Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL) Consist Of?
The GDL is a porous structure made by weaving carbon fibers into a carbon cloth (e.g. W1S1011 and ELAT) or by pressing carbon fibers together into a carbon paper (e.g. Sigracet, Freudenberg, and Toray). Many of the standard GDLs that are produced today come with a Micro Porous layer (MPL) and hydrophobic treatment (PTFE). The MPL and PTFE help with the contact with the membrane and with water management. The MPL typically provides a smooth layer with plenty of surface area for the catalyst and good contact with the membrane. The MPL often uses PTFE as a binder that increases hydrophobicity, which helps keep the water within the membrane from escaping - drying out the membrane and causing higher resistance (lower performance). There is often an additional PTFE coating on the MPL surface to further augment this.
What Exactly Does a Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL) Do?
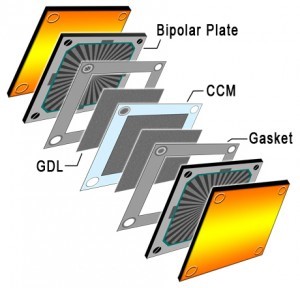
Gas Diffusion Layers essentially act as an electrode that facilitates the diffusion of reactants across the catalyst-layered membrane. The surface area and porosity of the GDL is what allow for the reactants in the channels of the bipolar plate to diffuse along the active area (catalyst area) of the membrane. With the increased surface area that the GDL provides, the transportation of electricity from each individual catalyst site in the Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) to the current collectors increases.
The GDL is also the component that handles the fuel cell moisture control. It does this by consistently helping to remove the by-produced water outside of the catalyst layer and prevent flooding chambers. The GDL also helps keep some water on the catalyst layer surface to improve conductivity throughout the membrane. It is also important to note that the GDL allows for heat transfer during cell operation as well.
Important considerations must also be made in regard to the mechanical properties of the GDL material since it is often compressed or partially compressed when the fuel cell stack is assembled. This compression can act as a bit of a "spring" to help accommodate for some of the thermal expansion larger fuel cell stacks can see in operation.
We found in our work that there was not a very good single source that compared the properties of the most common GDL materials (and the manufacturers often use different units and measures). We've compiled a Gas Diffusion Layer comparison table of some of the more common GDL materials so you can quickly compare properties and help decide which option might be best for you.
Which Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL) is right for you will depend on the specifics of how your fuel cell hardware, MEAs, and sealing are all designed. You can see our GDL Comparison Chart, here, to help narrow down the options




















Enter the code in the box below: