
Carbon Paper Gas Diffusion Layers
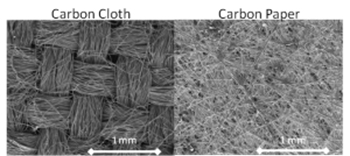
Carbon Paper Gas Diffusion Layers (GDLs) (e.g. Sigracet, Freudenberg, Toray, etc) tend to be thinner and more brittle than Carbon Cloth Gas Diffusion Layers (e.g. ELAT™, AvCarb , CT Carbon Cloth with MPL, etc.). Each variation has different mass transport, porosity, hydrophobicity and conductivity, among other things. Every manufacturer releases their own technical data sheet, so trying to parse all the information and find like qualities can be quite time-consuming and difficult. We have broken down the information into an easily digestible Gas Diffusion Layer Comparison Chart.
Carbon papers such as Toray are quite rigid and brittle, with very little compressibility (usually less than 10% of the GDL thickness. These are good for designs where a tighter tolerance is permitted in the compression and where the thin GDL is a critical factor. Since they are so brittle, care must be taken when handling them in order to not break corners or otherwise damage the GDL.
There are a few other carbon paper-based GDLs, which are much more flexible than Toray Paper (e.g. Sigracet and Freudenberg) and have a little more compressibility than Toray paper (up to 20% of the GDL’s thickness). This, in turn, makes them much easier to handle. They also do not chip or break as easily as Toray paper while still being available in thin sizes. Also, papers may or may not have Microporous Layers (MPL) and/or additional hydrophobic (Teflon) coatings.
The electrical conductivity of carbon paper products is usually higher than that of their carbon cloth counterparts. This is a product of the graphitic structure of the carbon papers, whereas the carbon cloths are a much more amorphous carbon structure.
Carbon Cloth Gas Diffusion Layers
The Carbon Cloth based GDL materials (e.g. W1S1011, ELAT LT 1400, ELAT LT 2400) are the most flexible and are generally quite mechanically robust, but are also quite a bit thicker than carbon paper GDLs. These are typically designed to have a fair amount of compression when assembled in the stack (anywhere from ~10% to 60% of the GDL thickness) and can act somewhat as compressible "springs" in the stack design.
Fuel Cell Store also offers a wide variety of carbon and graphite felt Gas Diffusion Layers, though these do not have application in the fuel cell and electrolyzer space, as much as they do in the battery space.
We've put together a convenient table listing the properties of all the carbon-based GDL materials offered by Fuel Cell Store. We hope it is useful in helping you make your selection. Of course, you're always welcome to email us at sales@fuelcellstore.com if you need more specific guidance in your application. There are many other GDL material types available, as well as custom options, that we are more than happy to assist you with.













Enter the code in the box below: